RefCirc (Reference CircRNAs database) is a manually curated database for circRNAs validated by experiments.
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are RNA molecules in which a covalent and canonical linkage termed a “backsplice” has formed between a downstream 3' splice site and an upstream 5' splice site in a linear pre-messenger RNA. Thousands of circRNAs have been discovered in various organisms.
CircRNAs often contain miRNA binding sites allowing them to interact with miRNAs. CircRNAs usually act as “miRNA sponge” to sequester the function of miRNAs so they can no longer act on their target mRNA. CircRNAs also interact with proteins to regulate gene expression and ultimately protein translation. The molecular mechanisms of most circRNAs in gene regulation remain to be explored.
CircRNAs have been shown to be both abundant and stable, and have been emerging as potential therapeutic targets for many human diseases, especially cancers.
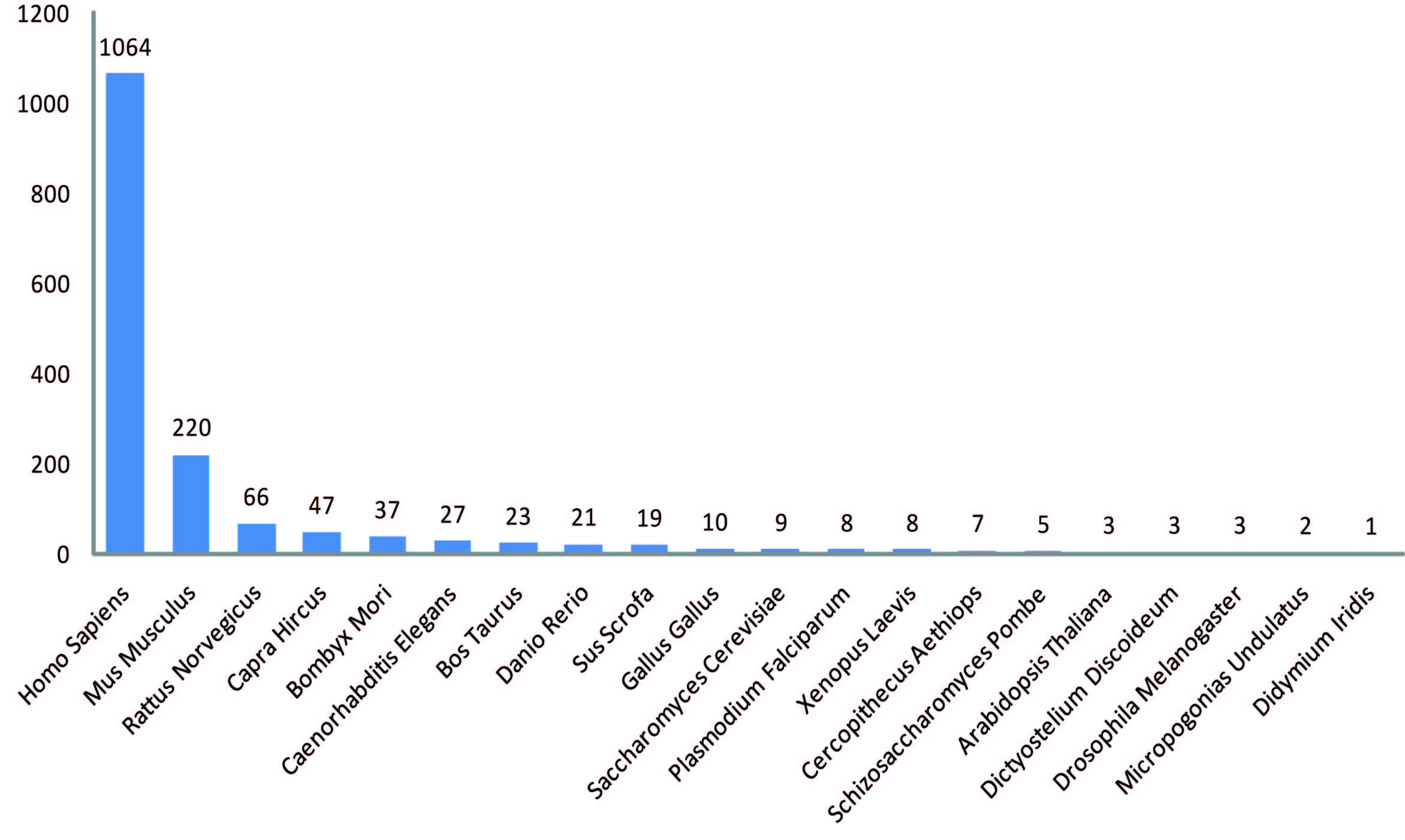
RefCirc is devoted to curating experimentally validated circRNAs. Currently, RefCirc contains 1583 circRNAs in 20 species collected from 342 published papers.
About circRNA
In 2012, genome-wide analysis of splicing led to the discovery of the global expression of circRNAs in eukaryotes. CircRNA constitutes the major isoform in hundreds of human genes. The primary products of transcription, pre-messenger RNAs (pre-mRNAs), undergo either canonical linear splicing to produce linear RNA or backsplicing and circularisation to produce circRNAs. Backsplicing is a spliceosome-mediated process which involves the joining of a downstream 5′ splice site to an upstream 3′ splice site to form a circRNA. Figure from Linda Szabo and Julia Salzman, 2016.
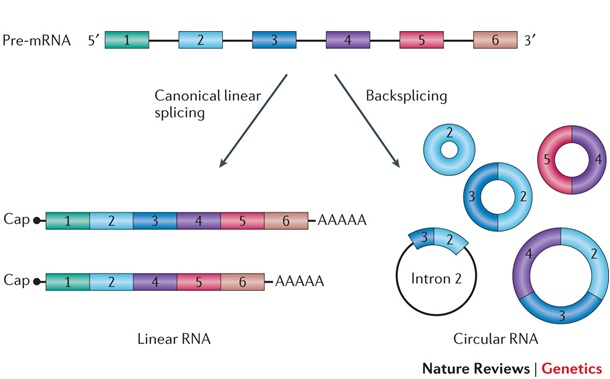
CircRNA Biogenesis
Three pathways generating circRNAs have been suggested so far. One model of biogenesis involves the presence of complementary sequence motifs in the introns flanking the exons to be circularized. In another model interaction between RBPs bound to sequence motifs in both introns flanking the exon(s) to be circularized facilitate the head-to-tail end-joining. In a third model of biogenesis exon skipping leads to mRNA consisting of exons 1 and 4 as well as a lariat structure containing the skipped exons 2 and 3. Figure from Karoline K. Ebbesen, et al. 2015.
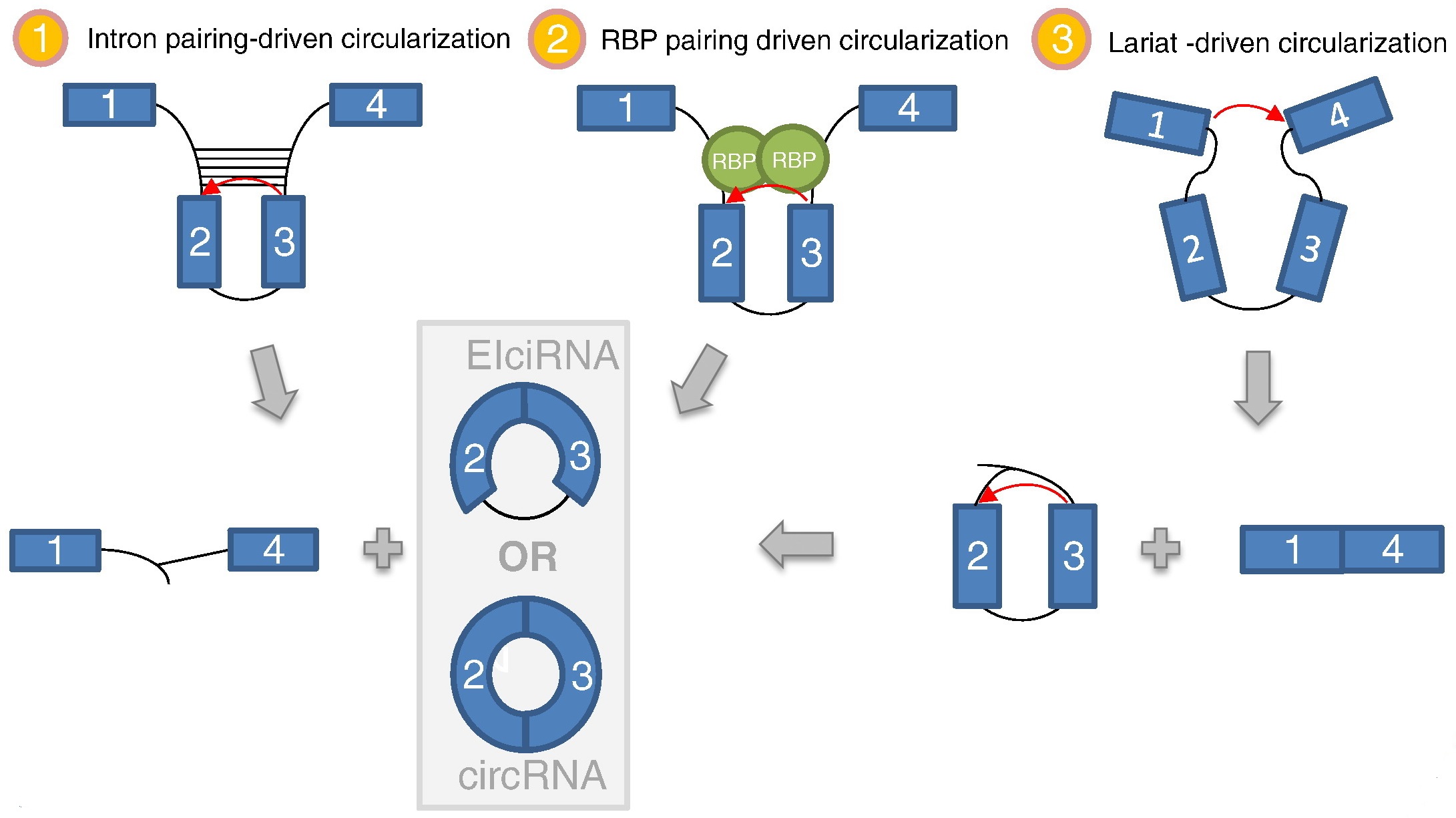
CircRNA Function
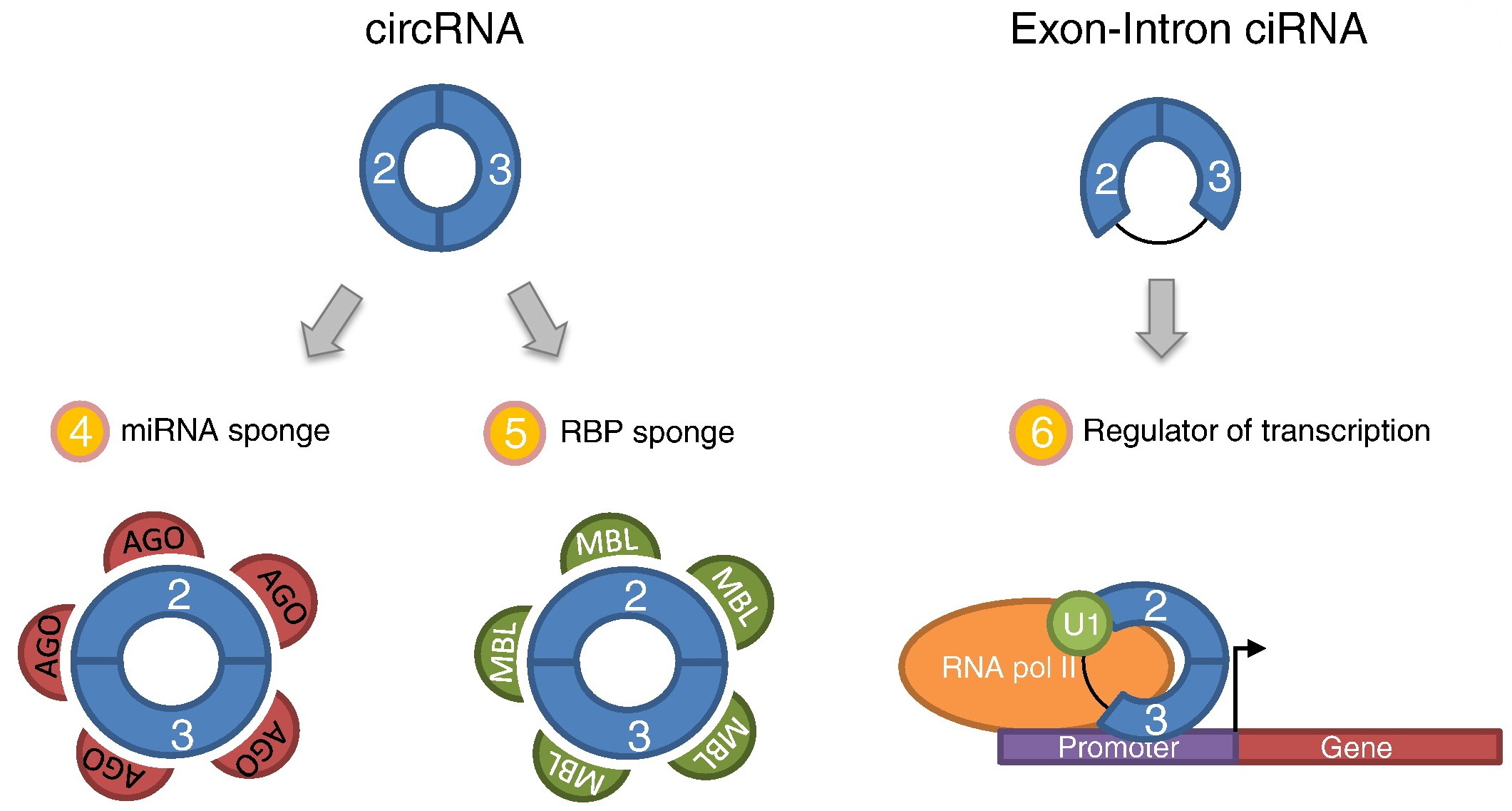
The known functions of circRNAs consist of miRNA regulation through sequestration of AGO-miRNA complexes if the circRNA contains miRNA binding sites or as a regulator of RBPs, as observed for Muscleblind (MBL) through binding of MBL to sites present in the circRNA. In contrast, exon–intron circRNAs are retained in the nucleus and function to promote transcription of their host genes through direct interaction with U1 snRNP mediated by the 5′ splice site within the retained intron. The exon–intron circRNA-U1 complex recruits RNA polymerase II to the promoter of the host gene which stimulates transcription initiation. Figure from Karoline K. Ebbesen, et al. 2015.
CircRNA databases
circBase: a database for circular RNAs.
CSCD: a database for cancer-specific circular RNAs.
exoRBase: a database of circRNA,lncRNA and mRNA in human blood exosomes.
circNet: a database of circular RNAs derived from transcriptome sequencing data.
circRNADb: A Database for Human Circular RNAs.
AtCircDB: a tissue-specific database for Arabidopsis circular RNAs.

RefCirc statistics
Currently, RefCirc contains 1583 circRNAs in 20 species.